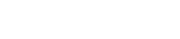
T2 weighted axial images
Megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts (Van der Knaap disease): A rare case report
SectionNeuroradiology
Case TypeClinical Cases
AuthorsYugandhara Shah, Chethan Belgur
Patient9 years, female
MR spectroscopic evaluation showed NAA/ Creatine ratio of 1.26 and Choline/ Creatine ratio of 1.14 which were within the normal range.
MRI brain is the investigation of choice. The MR findings are usually markedly abnormal and in typical cases often diagnostic [1]. MRI shows swollen white matter. There is bilateral, diffuse and extensive white matter hyperintensity on T2 W / T2 FLAIR sequence which appear hypointense on T1 weighted sequences, suggestive of extensive demyelination [1]. There is relative sparing of the central white matter structures like corpus callosum, internal capsules and brain stem [1]. The basal ganglia and the thalami are also spared [1, 3]. Subcortical cysts are seen across anterior temporal regions and also across the fronto-patietal region bilaterally [1].
Management consists of treatment of manifestations like Antiepileptic drugs (AED) if epileptic seizures are present, physical therapy to improve motor function, special education, speech therapy as needed [4].
[1] KV Rajagopal, RH Ramakrishnaiah, KR Avinash, BN Lakhkar (2006) Van der Knaap Disease, A megalencephalic Leukoencephalopathy. Ind J Radiol Imag 16:4:733-734
[2] Subhra Aditya , R Das Gupta, D Das, MK Roy, T Dhibar,T Das (2010) Van der Knaap syndrome, a case from West Bengal, India. Neurology Asia 15(2) : 193 – 195
[3] Paramdeep Singh, Kavita Saggar, Archana Ahluwalia, et al (2011) Teaching NeuroImages: Megaloencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts (Van der Knaap disease). Neurology- Americal Academy of Neurology 76;e34 (PMID: 21339493)
[4] Marjo S van der Knaap, MD, PhD and Gert C Scheper, PhD., (Augu) Megalencephalic Leukoencephalopathy with Subcortical Cysts. NCBI (PMID: 20301707)
| URL: | https://www.eurorad.org/case/11115 |
| DOI: | 10.1594/EURORAD/CASE.11115 |
| ISSN: | 1563-4086 |